How to Start, Stop, or Restart Apache Server on Ubuntu
Introduction
Apache is part of the popular LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack of software. It is included with the latest version of Ubuntu 18.04 by default.
This guide will show you how to start, stop, and restart the Apache service on Ubuntu using the terminal.
Prerequisites
- Access to a user account with sudo or root privileges
- An installed and configured Apache installation
- The apt package manager, included by default
- A command-line/terminal window (Ctrl-Alt-T)
Ubuntu 18.04, 16.04, and Debian 9.x Commands
Start Apache Web Server
For Ubuntu users with versions 16.04 and 18.04 and Debian 9.x users, use the following commands in the terminal window to start Apache:
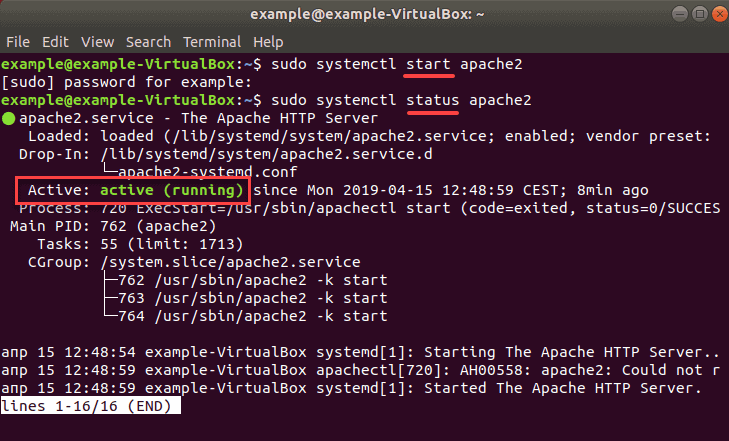
sudo systemctl start apache2Check status to see whether Apache is enabled with the command:
sudo systemctl status apache2If it is running, it should display the message active (running) as in the image below.
Stop Apache Web Server
Use the following commands in the terminal window to stop Apache:
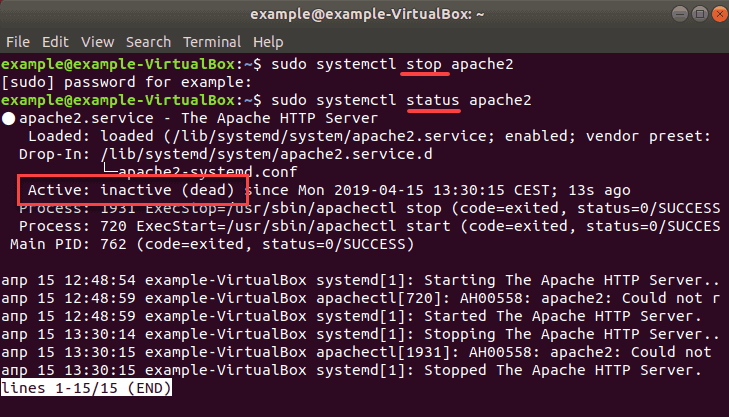
sudo systemctl stop apache2Check status to see whether Apache is disabled with the command:
sudo systemctl status apache2If it has stopped running, it should display the message inactive (dead) as in the image below.
Restart Apache Web Server
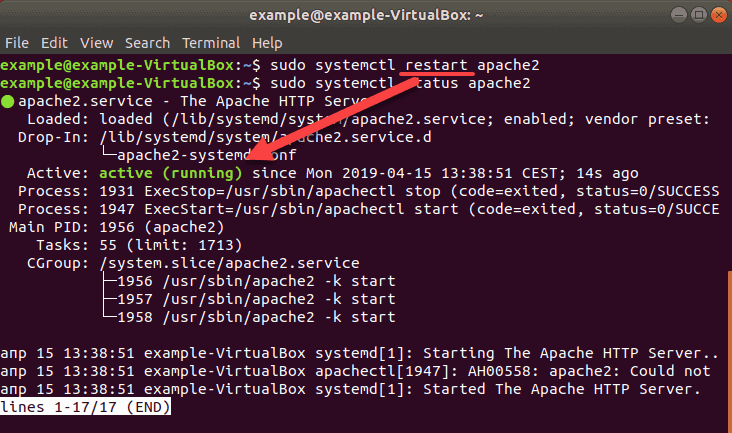
To restart Apache use the command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2If Apache was previously disabled, a status check will show that it is up and running again.
Ubuntu 14.10 or older Debian
Start Apache
For Ubuntu and Debian users with an older version, use the following commands in the terminal window to start Apache:
sudo service apache2 startor
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 startCheck status to see whether Apache is enabled with the command:
sudo service apache2 statusor
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 statusIt should display the message active (running).
Stop Apache
To stop Apache use the following command:
sudo service apache2 stopor
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 stopCheck status to see whether Apache is disabled with the command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 statusIt should display the message inactive (dead) as in the image below.
Restart Apache
To restart Apache use the command:
sudo service apache2 restartor
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restartNote: The restart command can take several moments to complete, depending on the complexity of your server configuration. If you’re running a large or complex server configuration, this can cause disruptions for users who rely on the server.
Conclusion
Starting, stopping, and restarting the Apache service on Ubuntu is straightforward. Knowing how to do these basic tasks from the terminal line makes the task faster and easier.


