How to Install and Configure Nginx from Source on Linux
Features of Nginx:
- It supports reverse proxy with caching.
- It supports WebSockets, load balancing, and fault tolerance.
- It supports FastCGI with caching.
- It can be used for handling static files, index files, and auto-indexing.
- It supports SSL.
- Both name-based and IP-based virtual servers can be configured in Nginx.
- HTTP basic authentication
- All the main mail proxy server features are supported in Nginx.
Installation of Nginx
Step 1: Download the Nginx archive from this link and save the archive file on your desktop.
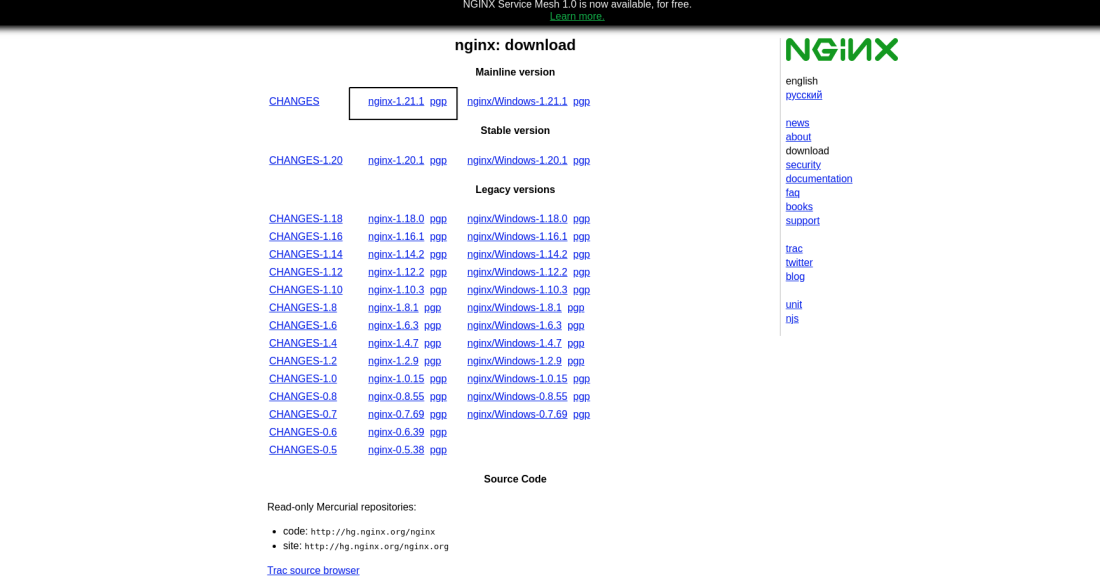
Nginx Download page
Or, you can download the Nginx web server archive file by running the following command in the terminal.
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.21.1.tar.gz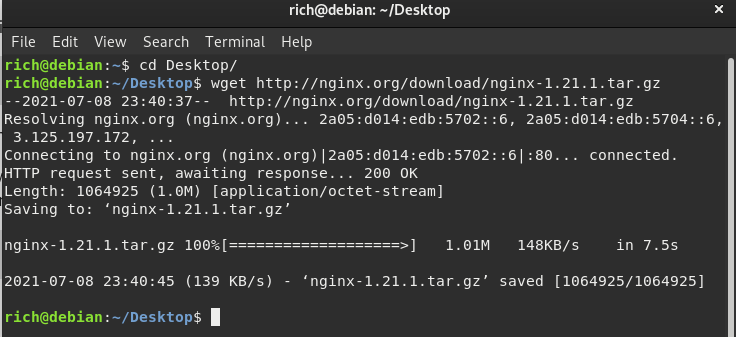
Downloading the Nginx server
Will fetch the archive file and save it to the location where you have opened the terminal.
Step 2: After downloading the archive, we need to navigate the folder where we have downloaded that archive and have to extract the archive using any archive utility. You can run the following command to extract the Nginx archive file.
tar -xf nginx-1.21.1.tar.gzAfter this, the folder structure should look like this.
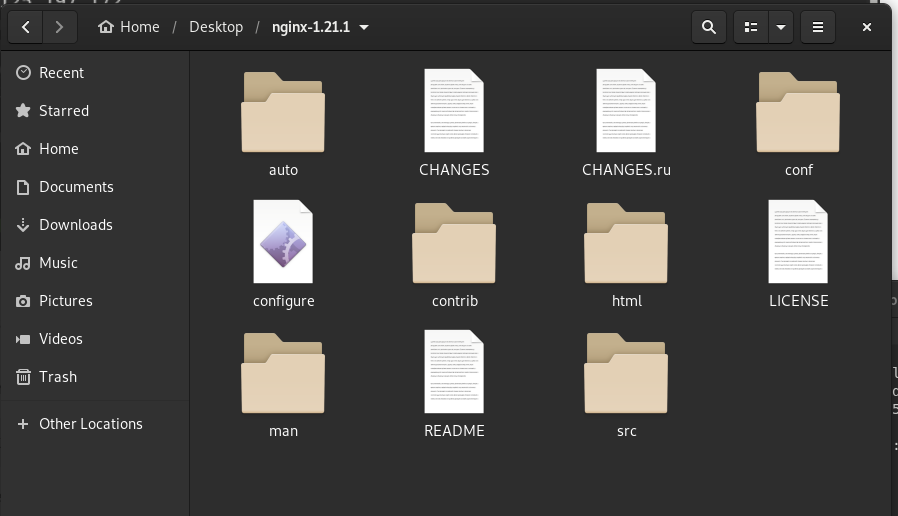
Nginx folder
Step 3: Now, to begin the installation of Nginx, navigate to the extracted folder and open the terminal here, then run the following command.
- Navigate to the directory by running the following command:
cd ~/Desktop/nginx-1.21.1- Start the configuration installer of the Nginx.
- ./configure
Here below is a summary of the configuration file:
Configuration summary
+ using system PCRE library
+ OpenSSL library is not used
+ md5: using system crypto library
+ sha1: using system crypto library
+ using system zlib library
nginx path prefix: "/usr/local/nginx"
nginx binary file: "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
nginx configuration prefix: "/usr/local/nginx/conf"
nginx configuration file: "/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf"
nginx pid file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
nginx error log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log"
nginx http access log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log"
nginx http client request body temporary files: "client_body_temp"
nginx http proxy temporary files: "proxy_temp"
nginx http fastcgi temporary files: "fastcgi_temp"
nginx http uwsgi temporary files: "uwsgi_temp"
nginx http scgi temporary files: "scgi_temp"- Build the Nginx package from the source using the make command.
make- Run the make install command to install the built package.
sudo make installThis command will install Nginx in the /usr/local/nginx directory.
Step 4: Confirm the installation and check the installed version of Nginx by running the following command:
Navigate to /usr/local/nginx using the cd command (change directory):
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbinTo check what is the currently installed version of the Nginx.
./nginx -v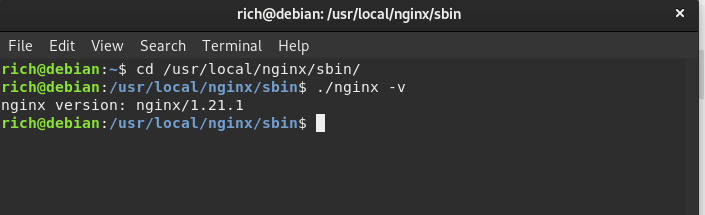
Successfully installed Nginx
Starting the Ngnix server
Follow the following steps to start an Nginx server.
- Navigate to the default location where Nginx is installed by running the following command in the terminal.
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin2. Now, we can start the Nginx server by running the following command:
sudo ./nginxTo see if it’s working, go to the localhost or your URL.
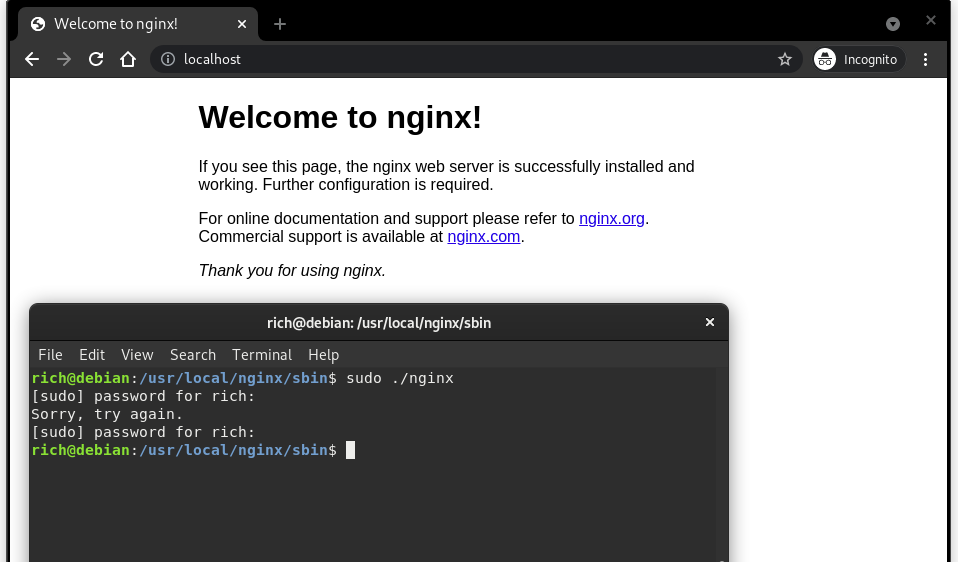
Nginx start (Welcome page)
Change the default Nginx listen port
By default, the Nginx is configured to listen on port 80. If you want to change the default Nginx listening port, you can do that by reconfiguring the nginx.conf file located under /usr/local/nginx/conf.
Steps to change the default Nginx Listen Port.
Step 1: Open the nginx.conf file by running the following command:
sudo nano /usr/local/nginx/confStep 2: After opening, the nginx.conf file should look like this:
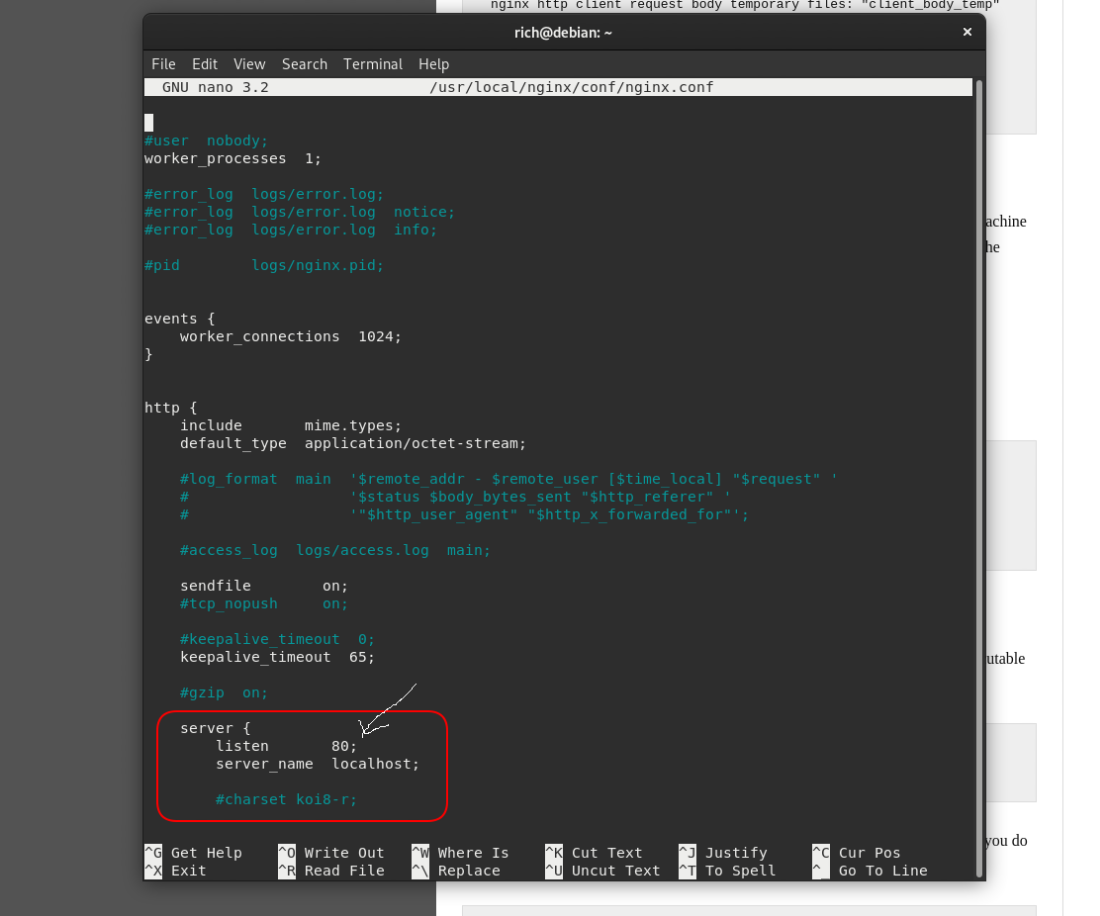
configuring listen port
Navigate to this server section and change listen 80; port to any other port number, e.g. 5555, etc.
Step 3: Save the file and run open the localhost with port 5555 as follows.
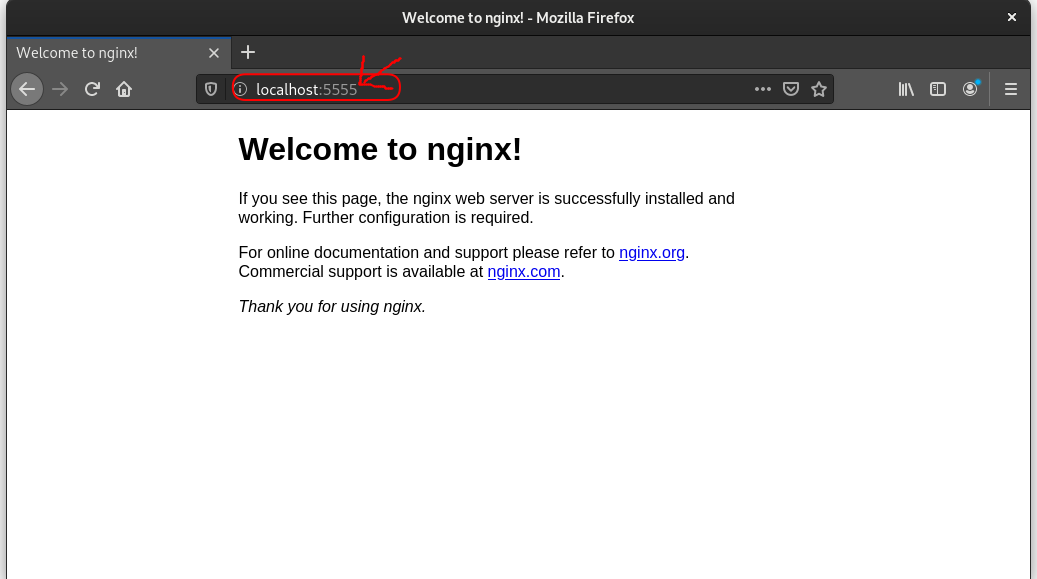
custom listen port
Stopping the Nginx server
To stop the Nginx server, we just need to add the flag -s to stop the Nginx command as follows.
sudo ./nginx -s stopThis will stop the Nginx server, you can refresh the localhost page and see.
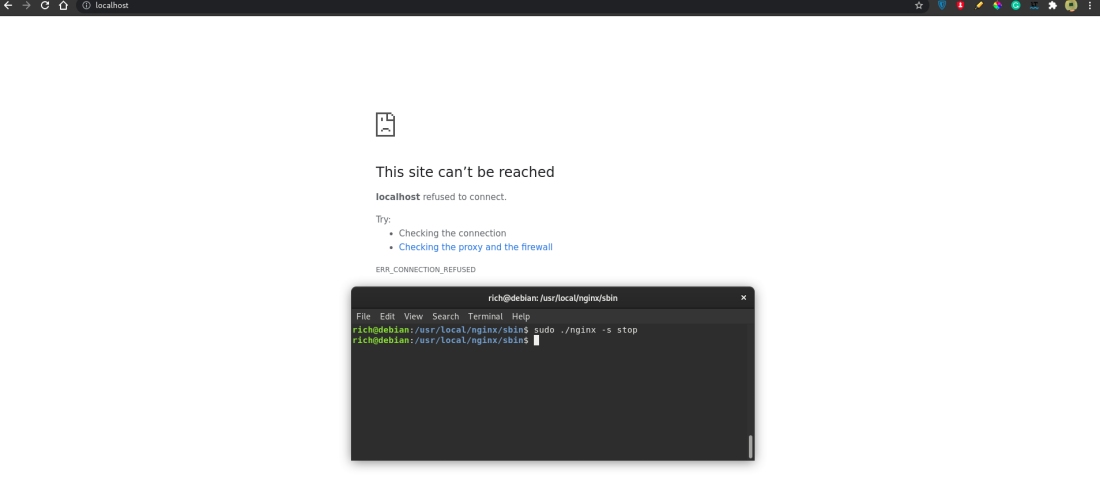
Nginx stop
Uninstalling the Nginx server
To uninstall Nginx, run the following command in the terminal with superuser permissions, i.e. sudo :
sudo rm -f -R /usr/local/nginx && rm -f /usr/local/sbin/nginx
This will completely remove Nginx from your machine. Here, we are using the rm command to remove the directories and subdirectories using -f and -R flags. -f is used to remove the directories, and -R will recursively remove all the directories within directories. Using &&, we can write multiple commands in a single line.

